패키지 관리자 update upgrade 차이
패키지 관리자는 리눅스에서 소프트웨어 패키지 설치를 간편하게 할 수 있도록 도와주는 명령어 인터페이스입니다.
대표적으로 레드햇(RedHat) 계열의 운영체제나 CentOS에서는 Yum(Yellow dog Updater, Modified)이 있으며 데비안(Debian) 계열이나 우분투(Ubuntu) 운영체제에서는 APT(Advanced Packaging Tool)가 존재합니다.
Yum과 APT에는(물론 다른 패키지 관리자에서도 존재할 수 있지만) update와 upgrade라는 명령어가 존재합니다. 예를 들면 다음과 같이 사용됩니다.
[root@localhost ~]# yum update 또는 [root@localhost ~]# apt upgrade
언뜻 보면 update와 upgrade 명령어의 큰 차이점은 없어보입니다. 그렇다면 이 둘의 실질적인 차이점은 무엇일까요?
apt를 사용할 때와 yum을 사용할 때 update와 upgrade 명령어는 서로 다른 역할을 합니다. 아래에 각 패키지 관리자별 업데이트 명령어 차이점을 정리해보았습니다.
apt update upgrade 차이
먼저 apt에서 update는 단순히 패키지 업데이트가 존재하는지 저장소 경로를 통해 확인 작업을 거칩니다. 다시 말해 apt update는 저장소 업데이트 작업만 진행합니다.
[root@localhost ~]# apt update Hit:1 http://kr.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic InRelease Hit:2 http://kr.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic-updates InRelease Hit:3 http://kr.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic-backports InRelease Hit:4 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic-security InRelease Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done 17 packages can be upgraded. Run 'apt list --upgradable' to see them.
실제로 패키지를 최신 패키지로 변경하는 작업은 apt upgrade를 입력해야 진행됩니다. 만약 apt update만을 입력했다면 실제 설치 파일은 변경되지 않으며, 만약 업데이트해야 할 내용들이 있을 경우 사용자에게 알리기만 합니다.
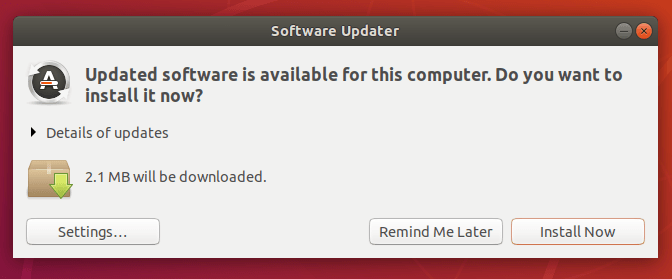
데스크톱에서는 apt update 명령어를 사용하지 않아도 Software Updater 소프트웨어에 의해 자동으로 체크될 것입니다. 다음과 같이 apt update를 입력한 것처럼 나타날 것입니다.
만약 apt upgrade 명령어를 사용하면, 패키지는 새로운 업데이트 내용에 따라 변경될 것입니다.
[root@localhost ~]# apt upgrade Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done Calculating upgrade... Done The following packages will be upgraded: bsdutils fdisk gir1.2-snapd-1 gnome-mines libblkid1 libfdisk1 libmount1 libsmartcols1 libsnapd-glib1 libuuid1 mount python3-distupgrade rfkill ubuntu-release-upgrader-core ubuntu-release-upgrader-gtk util-linux uuid-runtime 17 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded. Need to get 2,115 kB of archives. After this operation, 60.4 kB of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] Y Get:1 http://kr.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic-updates/main amd64 bsdutils amd64 1:2.31.1-0.4ubuntu3.2 [60.3 kB] Get:2 http://kr.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic-updates/main amd64 libuuid1 amd64 2.31.1-0.4ubuntu3.2 [20.0 kB] Get:3 http://kr.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic-updates/main amd64 libblkid1 amd64 2.31.1-0.4ubuntu3.2 [124 kB] ...(생략)
요약하자면 다음과 같습니다.
- apt update : 패키지 저장소를 통해 업데이트 파일이 있는지 확인
- apt upgrade : 패키지를 새로운 파일로 업데이트
yum update upgrade 차이
그러나 yum에서의 update와 upgrade 명령어는 apt와는 다릅니다. yum을 사용하면 yum update와 yum upgrade 명령어 모두 패키지의 실제 업데이트 작업을 수행합니다.
yum upgrade는 yum update에 -obsoletes 옵션을 붙인 것과 같습니다. 이는 패키지가 업데이트되면서 더 이상 사용되지 않는 관련된 파일이나 패키지를 삭제하게 됩니다. 기호에 따라 달라지겠지만 yum update -obsoletes 또는 yum upgrade를 사용하는 것이 권장되는 방법이 아닐까 싶습니다.
man 페이지에서도 다음과 같이 설명되어 있습니다.
update
If run without any packages, update will update every currently installed package. If one or more packages or package globs are specified, Yum will only update the listed packages. While updating packages, yum will ensure that all dependencies are satisfied. (See Specifying package names for more information) If the packages or globs specified match to packages which are not currently installed then update will not install them. update operates on groups, files, provides and filelists just like the "install" command.
upgrade
Is the same as the update command with the --obsoletes flag set. See update for more details.
요약하자면 다음과 같습니다.
- yum update : 패키지 업데이트 여부 확인 후 새로운 파일로 수정
- yum upgrade : 패키지 업데이트 여부 확인 후 새로운 파일로 수정





추가 : macOS의 brew 또한 Ubuntu의 동작과 같습니다.
– brew update : 패키지 저장소 업데이트
– brew upgrade : 실제 패키지 업데이트
감사합니다 정리가 아주 잘 되어 있네요
도움이 되어 다행입니다 🙂
정보 감사합니다 한가지 센트/데비안 둘다 업그레이드 할 경우 패키지와 + 커널까지 같이 업데이트 되는거죠??
네, 대부분 커널 업데이트 까지 체크하지만 데비안의 경우는 강제하지 않을 때도 있습니다.
또한 운영체제 상황에 따라 커널 업그레이드를 시도하지 않는 경우도 있습니다. 감사합니다.